Understanding Commodity Trading
Commodity trading involves buying and selling goods that are either extracted from the ground (like gold and oil) or cultivated (such as corn and coffee). The commodity market is known for its volatility, which can offer substantial opportunities for traders. It’s vital for traders to comprehend the factors that influence commodity prices, including supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and currency fluctuations.
Commodity Trading Platforms
A critical step for any trader is choosing the right commodities trading platform. The ideal platform should offer a range of commodities, analytical tools, real-time market data, and educational resources. It should also be user-friendly and provide robust security measures. Many platforms also offer demo accounts, allowing new traders to practice without financial risk.
Commodity Futures Trading
One of the most popular methods of commodity trading is through commodity futures. Futures are contracts to buy or sell a specific quantity of a commodity at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future. They can be used for hedging against price changes or for speculative purposes. Understanding how futures work and the risks involved is essential for anyone considering this approach.
Top Commodity Trading Strategies
- Fundamental Analysis: This involves analyzing factors like weather patterns, government policies, and global economic indicators that affect the supply and demand of commodities. For instance, a drought can reduce the supply of agricultural commodities, potentially driving up prices.
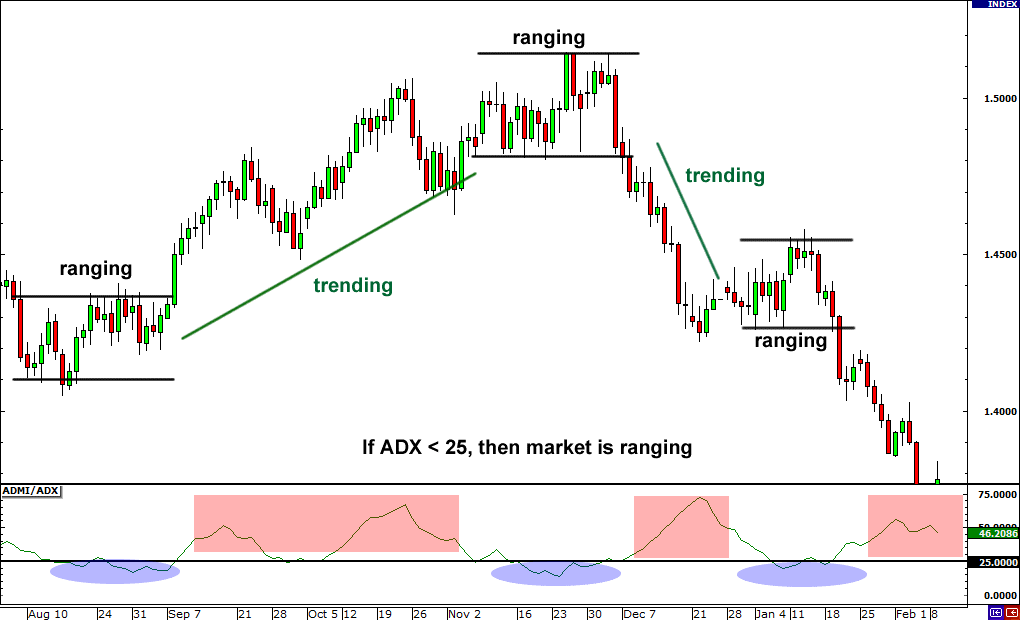
- Technical Analysis: This strategy uses historical market data and statistical techniques to predict future market trends. Chart patterns, price trends, and volume analysis are commonly used tools in this approach.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various commodities can reduce risk. Different commodities often react differently to the same economic event, so diversification can provide a buffer against market volatility.
- Trend Following: This strategy involves identifying and following market trends. Traders buy commodities in a rising market and sell them in a falling market. While straightforward, it requires discipline and close market monitoring.
- Range Trading: In this strategy, traders identify commodities that are trading within a consistent range and buy at the lower end of that range and sell at the higher end. This works well in markets with less volatility.
- Scalping: A strategy used in day trading where traders make quick, small profits on minor price changes. It requires a significant amount of time and attention, as well as a deep understanding of market movements.
- Hedging: Often used by producers or consumers of commodities, hedging involves taking an offsetting position in a commodity to protect against price changes. For example, an airline company might use futures contracts to hedge against rising oil prices.
Risk Management in Commodity Trading
Effective risk management is crucial in commodity trading due to its inherent volatility. Setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, monitoring global events impacting commodities, and understanding the leverage involved in futures trading are essential practices.
Conclusion
Commodity trading offers a unique avenue for investors to diversify their portfolios and tap into different market dynamics. By employing strategies like fundamental and technical analysis, diversification, and effective risk management, traders can navigate the complexities of the commodity market. As with any trading, education, and continuous market analysis are key to achieving success in the vibrant world of commodity trading.